Operators and Input
Operators are special symbols in Python that carry out arithmetic or logical computation. The value that the operator operates is called the operand.
Python divides the operators in the following groups:
Arithmetic operators
| Operator | Name | Example |
|---|---|---|
| + | Addition | x + y |
| - | Subtraction | x - y |
| * | Multiplication | x * y |
| / | Division | x / y |
| % | Modulus | x % y |
| ** | Exponentiation | x ** y |
| // | Floor division | x // y |
x = 15
y = 4
# Output: x + y = 19
print('x + y =',x+y)
# Output: x - y = 11
print('x - y =',x-y)
# Output: x * y = 60
print('x * y =',x*y)
# Output: x / y = 3.75
print('x / y =',x/y)
# Output: x // y = 3
print('x // y =',x//y)
# Output: x ** y = 50625
print('x ** y =',x**y)
Assignment Operators
Assignment operators are used in Python to assign values to variables.
| Operator | password |
|---|---|
| = | x = 5 |
| += | x += 3 |
| -= | x -= 3 |
| _= | x _= 3 |
| /= | x /= 3 |
| %= | x %= 3 |
| //= | x //= 3 |
| **= | x **= 3 |
| &= | x &= 3 |
| |= | x| = 3 |
| ^= | x ^= 3 |
| »= | x »= 3 |
| «= | x «= 3 |
Comparison Operators
Comparison operators are used to compare values. It returns either True or False according to the condition.
| Operator | Name | Example |
|---|---|---|
| == | Equal | x == y |
| != | Not equal | x != y |
| > | Greater than | x > y |
| < | Less than | x < y |
| >= | Greater than or equal to | x >= y |
| <= | Less than or equal to | x <= |
Logical Operators
Logical operators are the and, or, not operators.
| Operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| and | Returns True if both statements are true | x < 5 and x < 10 |
| or | Returns True if one of the statements is true | x < 5 or x < 4 |
| not | Reverse the result, returns False if the result is true | not(x < 5 and x < 10) |
Identity Operators
is and is not are the identity operators in Python. They are used to check if two values (or variables) are located on the same part of the memory. Two variables that are equal does not imply that they are identical.
| Operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| is | Returns True if both variables are the same object | x is y |
| is not | Returns True if both variables are not the same object | x is not y |
Membership Operators
in and not in are the membership operators in Python. They are used to test whether a value or variable is found in a sequence (string, list, tuple, set and dictionary).
| Operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| in | Returns True if a sequence with the specified value is present in the object | x in y |
| not in | Returns True if a sequence with the specified value is not present in the object | x not in y |
Bitwise Operators
Bitwise operators act on operands as if they were strings of binary digits. They operate bit by bit, hence the name.
| Operator | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| & | AND | Sets each bit to 1 if both bits are 1 |
| | | OR | Sets each bit to 1 if one of two bits is 1 |
| ^ | XOR | Sets each bit to 1 if only one of two bits is 1 |
| ~ | NOT | Inverts all the bits |
| « | Zero fill left shift | Shift left by pushing zeros in from the right and let the leftmost bits fall off |
| » | Signed right shift | Shift right by pushing copies of the leftmost bit in from the left, and let the rightmost bits fall off |
Input
The input() function allows user input.
syntax
input(prompt)
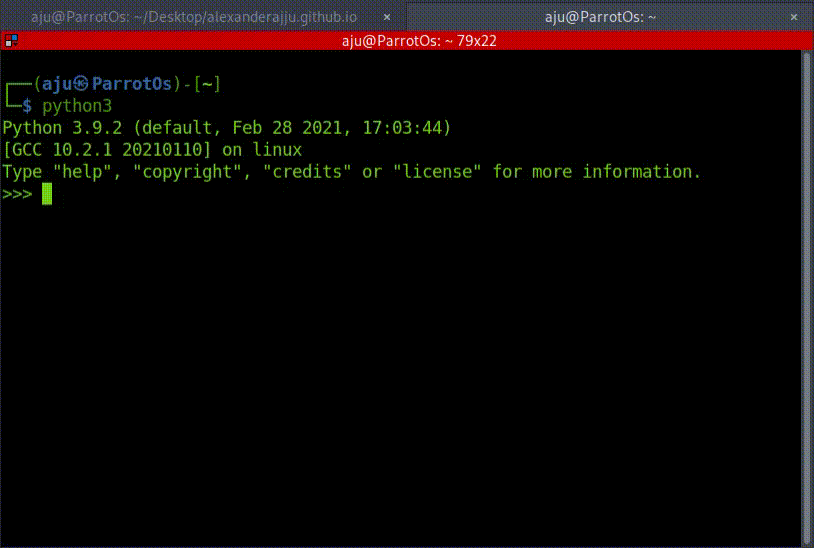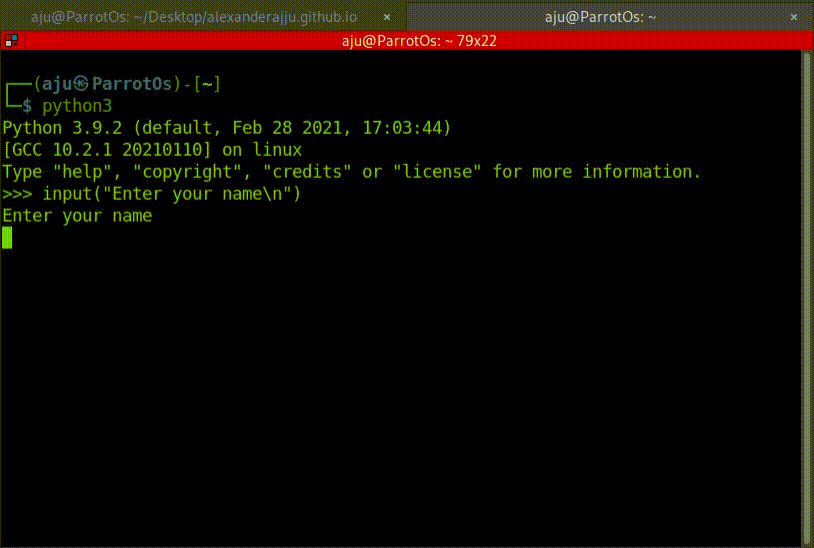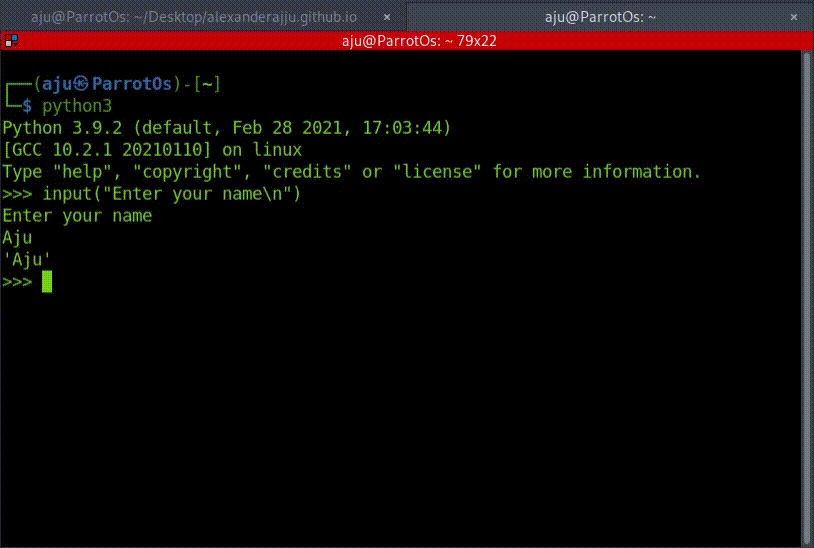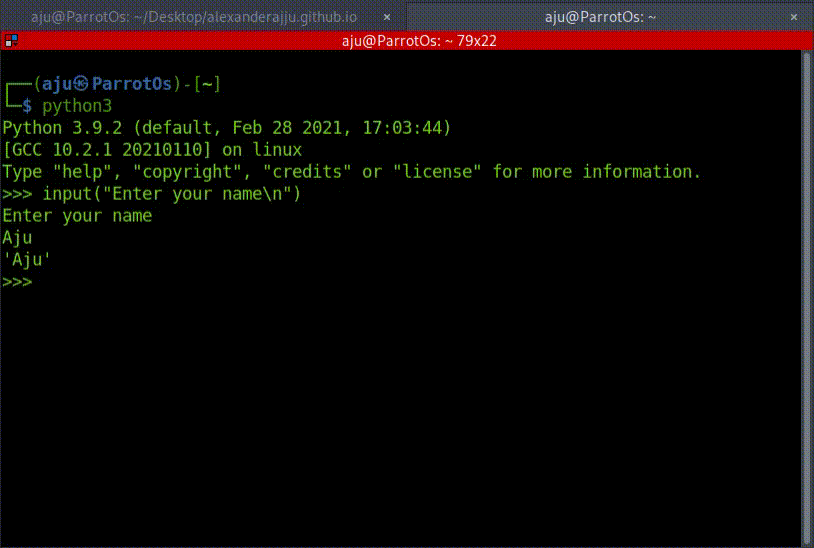
>>> input('Enter your name\n')
Enter your name
Aju
'Aju'